The blockchain is a public ledger made up of a sequence of blocks, which holds a full history of transaction records that occurred within the network. There are four types of blockchain systems now in use: public, private, consortium, and hybrid blockchains.
- Public Blockchains: Public blockchains feature a completely decentralized network in which every member has access to the blockchain information and may participate in the consensus process (e.g. Bitcoin and Ethereum).
- Private Blockchains: Private blockchains are designed for single enterprise solutions and are used to track data transactions between departments or people. Every participant needs permission to join the network and will be deemed a known member after it has been adhered to.

- Consortium Blockchains: A consortium blockchain is a permissioned network that is exclusively accessible to a certain set of people. It is utilized as an auditable and dependable synchronized distributed database that maintains track of data exchanges between participants.

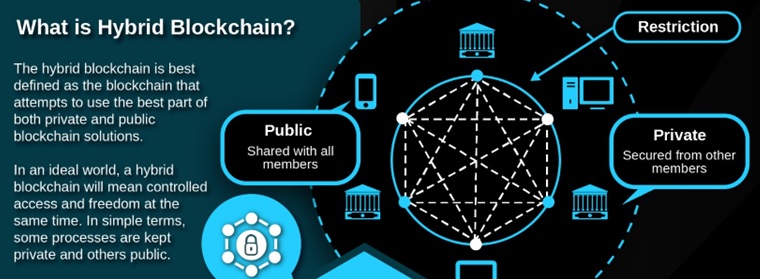
- Hybrid Blockchains: The advantages of both private and public blockchains are combined in hybrid blockchains. As a result, a public blockchain is used to make the ledger completely visible, with a private blockchain operating in the background to control access to the ledger’s modifications.
Sources:
