IP Spoofing is a hacker’s fake ID. . They are able to hide their identity and the real source of their device by using a fictitious IP address. Hackers can use IP spoofing to steal personal data, infect your device with malware, or bombard websites with DDoS attacks. Learn to recognize and stop IP spoofing attempts, then use a VPN to completely thwart them.
What is IP spoofing?
IP spoofing refers to the creation of IP (Internet Protocol) packets using a fake source IP address to impersonate — or spoof — another device. Once a fake IP address is seen as trustworthy, hackers can mine the victim’s device for sensitive information or launch an online attack.
Although it’s often used maliciously, IP spoofing itself it’s not a cybercrime — there are some legitimate reasons to spoof an IP. For example, online businesses often use spoofed IP addresses to test websites before they’re live.
When used for the purpose of an IP spoofing attack — like using a fake IP address to hack into servers to shut them down or steal data — IP spoofing is considered a cybercrime. Hackers can also use other forms of spoofing, like website or phone spoofing to collect personal info.
How IP spoofing works
IP spoofing works like this: a hacker uses code or other special tools to change the source IP address in the sent packet header, which is the collection of data required for an online message to reach its destination. This IP modification tricks the receiving computer into thinking the network packet is from a trustworthy source, so the packet (and data) is accepted.
IP Packets
Networked computers and other devices communicate by sending and receiving IP packets — data broken up into bits. When you request information on the internet, your device receives IP packets and reassembles them. This is how the internet works.
All IP packets contain a header with important routing information, like the source address or where the message originated. Normally, the source address is the IP address of the person or computer that sent the packet. During IP spoofing, the source address is a fake IP address that often mimics a trustworthy source.
IP spoofing attacks
Hackers can use tools to modify the source address of the IP packets they send. With a fake source address, hackers can appear like a trusted device on your network, then request sensitive information that your device will freely give away. Once they gain trust, hackers can also directly attack your device.
IP address spoofing attacks can be difficult to detect. They occur on a network level, so there aren’t any outward signs of tampering. And since the source address is false and randomized, it’s difficult to block these malicious requests or trace them back to their actual source.
Using privacy and security software can defend against IP spoofing attacks. Avast One — our comprehensive security tool with built-in antivirus, a VPN, and dedicated firewall protection — provides all these features and more to help safeguard your devices against IP spoofers and keep your data private.
Types of IP spoofing
IP spoofing can be used for a variety of attacks. Once hackers gain your device’s trust, they can use that vulnerability to request personal information, send a computer virus, or even turn your device into a zombie to support a large-scale bot attack on a target network. Here are the most common types of IP spoofing attacks:
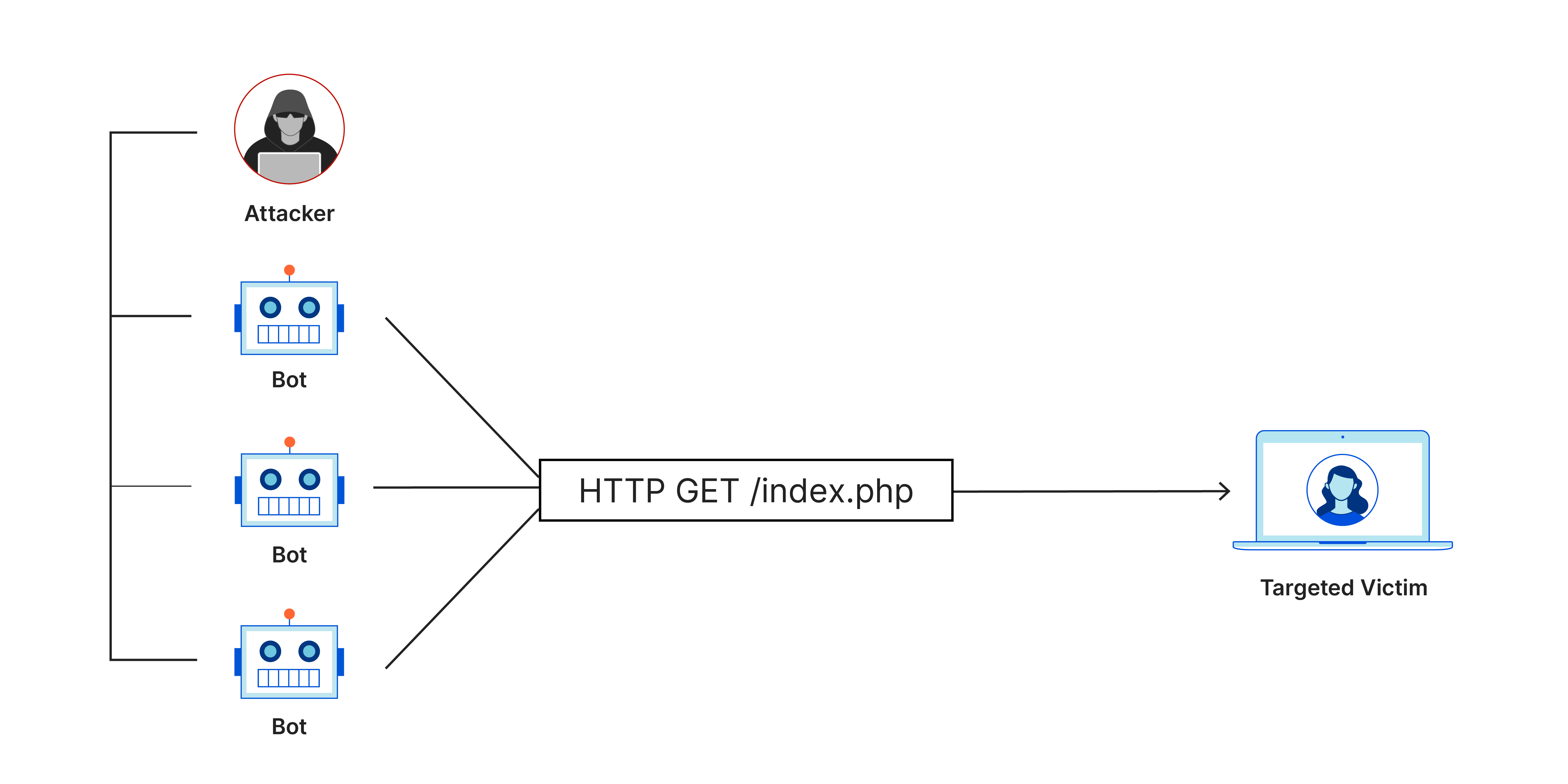
DDoS
A DDoS (distributed denial of service) attack works by overwhelming a network or server with traffic until it crashes. Hackers use IP packets containing fake IP addresses to blast networks or servers until they can’t keep up with the requests, crashing as a result.
The point of a DDoS attack is to flood a network or server until it’s unable to process requests and serve real visitors. And, since a DDoS attack uses IP spoofing, the false source address is also continually randomized, making it difficult for authorities to trace and stop.
Masking botnet devices
Botnets are networks of hacked computers that can be controlled remotely to spread malware, spam, or stage DDoS attacks. A single botnet can contain tens of thousands of computers.
In a DDoS attack, hackers often use botnets to send an overwhelming number of spoofed IP packets to a server. With the spoofed IP addresses, hackers can disguise the source addresses of their botnets, making it difficult to stop.
Man-in-the-middle
A man-in-the-middle attack occurs when hackers intercept communication between two computers that are unaware of the interference. It’s a common online threat that allows hackers to eavesdrop or even alter communication.
During an IP spoofing attack, hackers alter their IP address to trick your device into thinking they are legitimate. Using this IP spoofing method, man-in-the-middle attackers can intercept communication between two devices in order to quietly alter or steal IP packets. Your device may also freely give sensitive data to man-in-the-middle hackers, which they can use or sell on dark web marketplaces.
How to prevent spoofing
To help prevent IP spoofing, you should use a VPN to hide your IP address. Then, monitor your network for suspicious activity with a firewall, which uses a packet filter that inspects IP packet headers. Only visit secure sites that use HTTPS protocol, and make sure to use strong passwords everywhere possible.
there are some things you can do to stop spoofed IP packets from entering a network.
- Strong verification methods Tools like SSL certificates help verify websites trying to connect to your network.
- Firewalls Protect your network with a firewall to secure your device against unauthorized IP packets, fake source IP addresses, and suspicious traffic.
- The newest internet protocolsIPv6 vs IPv4 offers updated security protections.
- HTTPS websites with secure encryption protocols — like HTTPS — are generally safer. An online security browser extension can also help you detect dangerous websites while you browse.
- Strong passwords Creating strong passwords will help keep IP spoofers out of your devices.
- IP address authentication Using IP address authentication in place of other login data can help verify that users are who they say they are.
- A trustworthy antivirus By using one of the best free antivirus apps on the market, you have a better chance of catching any intruders trying to sneak into your network.
Conclusion
It enables individuals to cover up their identity and the actual source of their device by using a faked IP address. Hackers can use IP spoofing to infect your device with malware, steal personal information, or flood websites with DDoS attacks. Learn how to detect and stop IP spoofing attacks.